Is It Possible to Prevent Diabetes When Genetics Play a Role?
There are many different diseases that people get that because the genetic material for those diseases are passed down from generation to generation. Alzheimer’s is one such disease.
If you had a mother or father diagnosed with the disease, then your odds of getting it would be increased. However, some diseases will not automatically develop in the next family member – even if there is a history of the condition.
The reason for this is because at the root of some diseases is the ability to stop the condition from occurring. Diabetes is one of these conditions. It doesn’t matter if you had grandparents, parents or siblings diagnosed with diabetes.
You’re not doomed to get the condition if you’re proactive about it. That’s the key to preventing getting diabetes. Being proactive with your health. That means that you must take steps to do what you can so that the risk factors that go hand in hand with the disease don’t take control in your life.
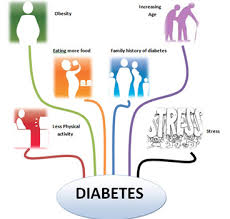
The biggest risk factor for getting the disease is how much weight that you carry. For each pound that you are overweight, it impacts your risk level for developing diabetes. The reason that this happens is because of how the body’s cells are impacted by the fat.
People who are overweight struggle to be able to properly use the insulin their body produces. The cells become resistant toward insulin rather than having the sensitivity that you would normally have.
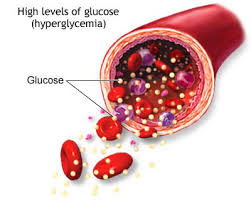
When your cells become insulin resistant, the glucose can build up in your bloodstream and lead to high sugar readings. This leads to organ damage, a higher risk of heart attacks, blindness, amputation and even premature death.
So if you are carrying extra weight and you have a family history of diabetes, lose weight so that you’re in the healthy zone for your height and frame. The second biggest risk to developing diabetes is the kind of foods that you eat.
If you eat a diet that’s high in calories and loaded with sugar, then your odds of getting the disease will increase. One thing about eating sugar is that it triggers a feel good hormone in the body, which can lead to craving even more sugar.
To keep diabetes at bay, it’s best to have a low carb, healthy meal plan. The third biggest risk to getting diabetes if you have a family history of the disease is being inactive.
If you spend more time sitting around watching television than you do being active, your chances of getting diabetes will increase. Exercise allows the body to be able to use the glucose properly and it keeps the cells from becoming insulin resistant. It also helps keep the extra weight off.